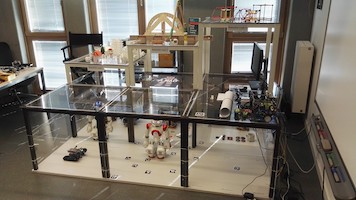
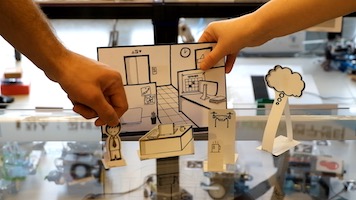
The OMILAB Node at the University of Vienna is a space to collaborate, innovate and engineer. Both a physical and virtual place, it is equipped with tools to explore method creation and design, experiment with method engineering and deploy software tools for modelling.
The work accomplished by the OMiLAB Vienna Node provides novel research results in the areas of Meta-Modelling, Semantic Technologies, Hybrid Method Engineering and Intelligent and Agile Agents.
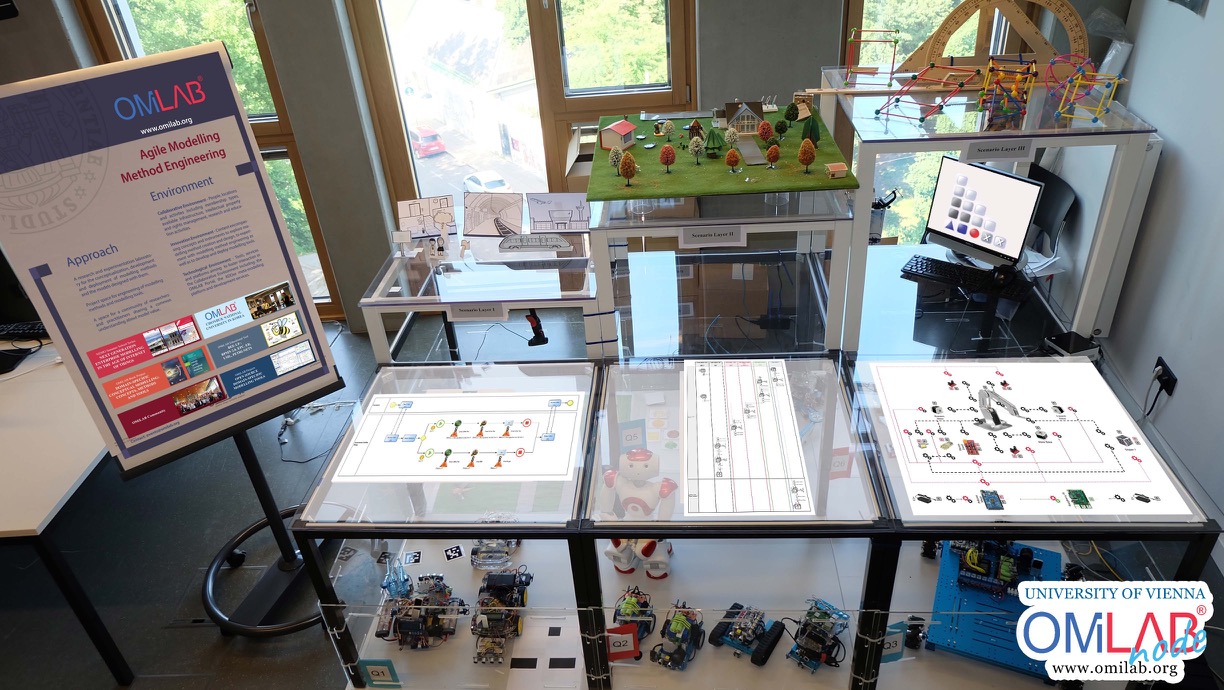

About the OMILAB Node
The Agile Modelling Method Engineering Framework is one of the core knowledge resources provided by the OMiLAB Vienna Node. Design Thinking is another valuable expertise of the node, enhanced by the development of the Scene2Model tool.
The work accomplished by the OMiLAB Vienna Node provides novel research results in the areas of Meta-Modelling, Semantic Technologies, Hybrid Method Engineering and Intelligent and Agile Agents.
Competences
- Meta-modelling
- Modelling Tool Engineering
- Digital Twin
- Agile Modelling Method Engineering
About the Hosting Organisation
Results
Get an overview what this OMiLAB has accomplised! Selected results are presented below as a contribution to the global community:
Bee-Up for Education

Scene2Model Modelling Toolkit

OMiLAB-Rob Experiments

MM-DSL Toolkit
Pro-Vis
All further results of the OMiLAB Node are via the organizer.
Activities
The following, selected activities are organized by the OMiLAB.
NEMO Summerschool
Domain-Specifc Conceptual Moodelling for Analysing Complex Digital Environments - An IoT-based Smart City Case
DigiFoF Project
Resources
The following cyber-physical resources are available at the OMILAB node:
Dobot Magician
The Dobot Magican demonstrates sorting and collaborative scenarios.
Makeblock mBot
This CPS is applied for smart mobility application scenarios.
Makeblock mBot Rover
The Rover provides additional sensors and a different operational setup, compared to the mBot Classic.
Mecanum wheel
A large mobile robot that demonstrates loading/unloading mechanisms as well as novel turning capabilities.
BeeBop Drone
Controlling a drone using models? Application scenarios from follow-me and smart tourist guides are realized using this CPS.
NAO
This humanoid robot provides demonstration capabilities for human-machine interaction. The OMiLAB node has two NAOs available for collaborative scenarios.
DrawBot
For design thinking scenarios, this CPS enables remote white-boarding.
Publications
Relevant publications of the OMILAB node: